Швидкі посилання
YOUBOLI AN Series In-Line Muffler AN10/AN15/AN20/AN30 Пневматичні деталі

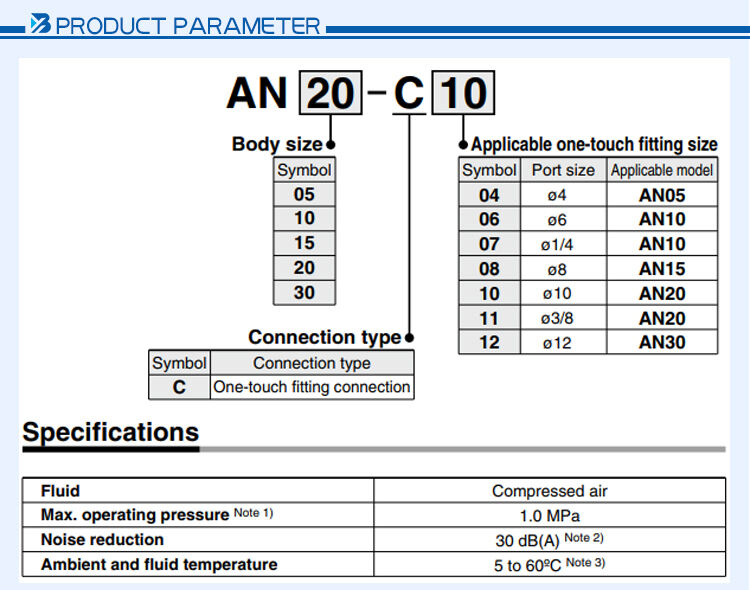
Пневматичний глушитель AN прямого підключення має наступні особливості:







Всі права захищені. Copyright © 2025 Youboli Pneumatic Technology Co., Ltd. - Політика конфіденційності